What Does Mouth Breathing Have to Do With ADHD and Why Does My Child Snore
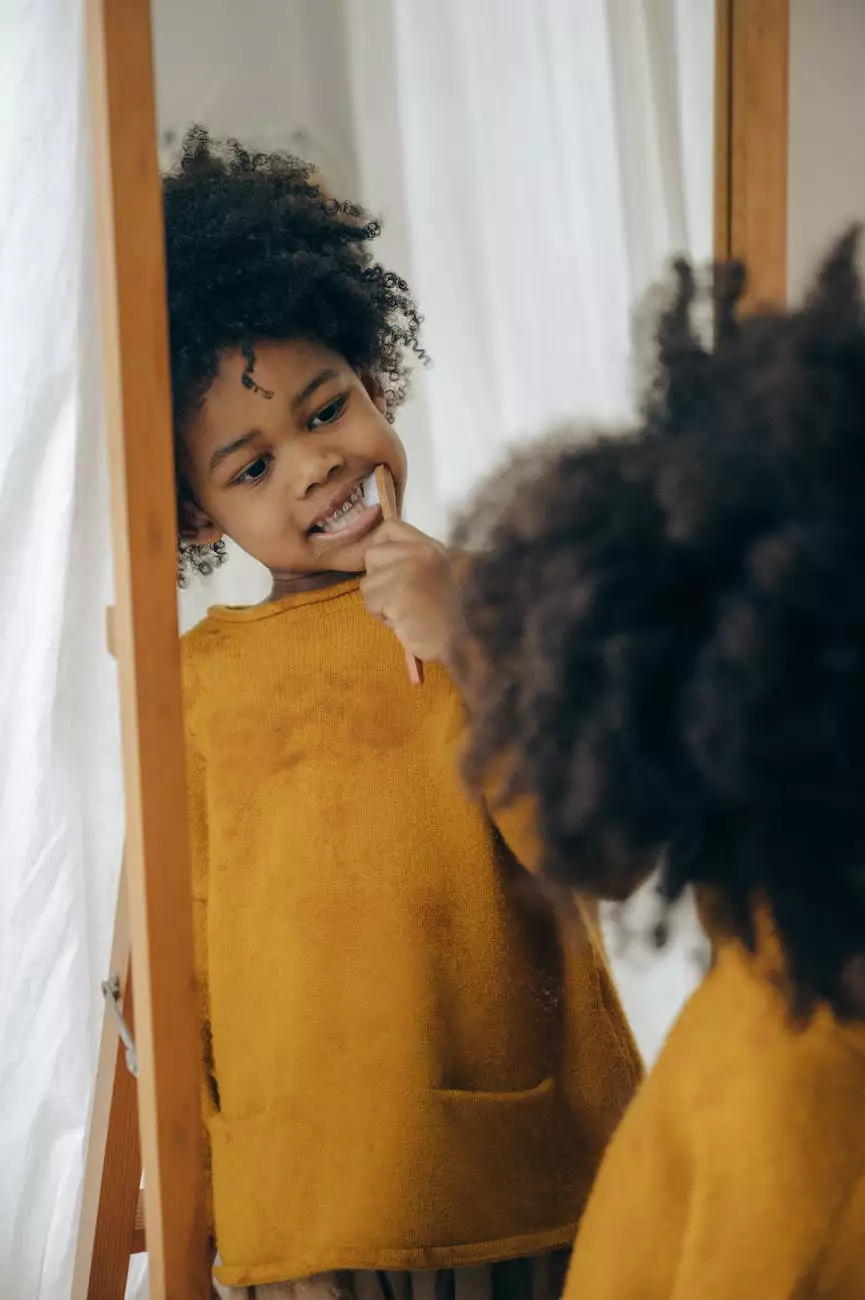

Introduction
Welcome to Michael Finley, CNHP, your trusted resource for understanding the connections between health conditions and holistic well-being. In this article, we explore the fascinating correlations between mouth breathing, Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), and snoring in children. We will delve into the effects of mouth breathing on sleep quality and cognitive function, offering valuable insights for parents and caregivers.
The Link Between Mouth Breathing and ADHD
Recent studies have shed light on the significant associations between mouth breathing and ADHD in children. Mouth breathing refers to the habit of breathing through the mouth rather than the nose, often due to nasal congestion or structural issues. When children consistently breathe through their mouths, it can lead to various health consequences, including an increased risk of developing or exacerbating ADHD symptoms.
The Impact on Sleep Quality
One of the key factors contributing to the mouth breathing-ADHD connection is the impact on sleep quality. Chronic mouth breathing during sleep can disrupt normal breathing patterns, leading to inadequate oxygen intake and elevated carbon dioxide levels. This oxygen deprivation can compromise the quality of sleep, making it difficult for children to achieve deep, restorative sleep stages.
The Role of Sleep Disordered Breathing
Snoring, a common symptom of sleep-disordered breathing, is frequently associated with mouth breathing. Sleep disordered breathing encompasses a range of conditions, including snoring, obstructive sleep apnea, and upper airway resistance syndrome. These conditions can interrupt the natural sleep cycle, potentially contributing to attention and behavioral issues commonly observed in children with ADHD.
Understanding the Effects on Cognitive Function
The impact of mouth breathing on cognitive function is a significant concern for parents. Insufficient sleep due to mouth breathing-related sleep disruptions can impair memory, attention, and overall cognitive performance. Lack of quality sleep can also lead to daytime drowsiness, irritability, and difficulty concentrating, which can further exacerbate ADHD symptoms and affect a child's academic performance and social interactions.
Identifying and Addressing Mouth Breathing
Recognizing the signs of mouth breathing is crucial for early intervention. Some common signs to watch for include dry mouth, cracked lips, pale gums, and daytime fatigue. If you suspect your child may be a mouth breather, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a holistic practitioner or pediatrician specializing in sleep disorders. They can help diagnose the underlying causes and recommend appropriate treatment strategies.
Treatment Options
The treatment approach for mouth breathing may vary depending on the underlying cause. In many cases, addressing nasal congestion and any structural abnormalities can help encourage nasal breathing. Treatment options may include nasal decongestants, allergy management, breathing exercises, and in some cases, surgical interventions. A holistic approach that considers the entirety of a child's health and well-being is beneficial for long-term success.
Conclusion
Understanding the correlation between mouth breathing, ADHD, and snoring is crucial for parents seeking to optimize their child's health and well-being. By addressing mouth breathing concerns early on and ensuring adequate sleep quality, parents can positively influence their child's cognitive function, behavior, and overall quality of life. For personalized advice and comprehensive support, contact Michael Finley, CNHP, today, and take the first step towards a healthier future for your child.